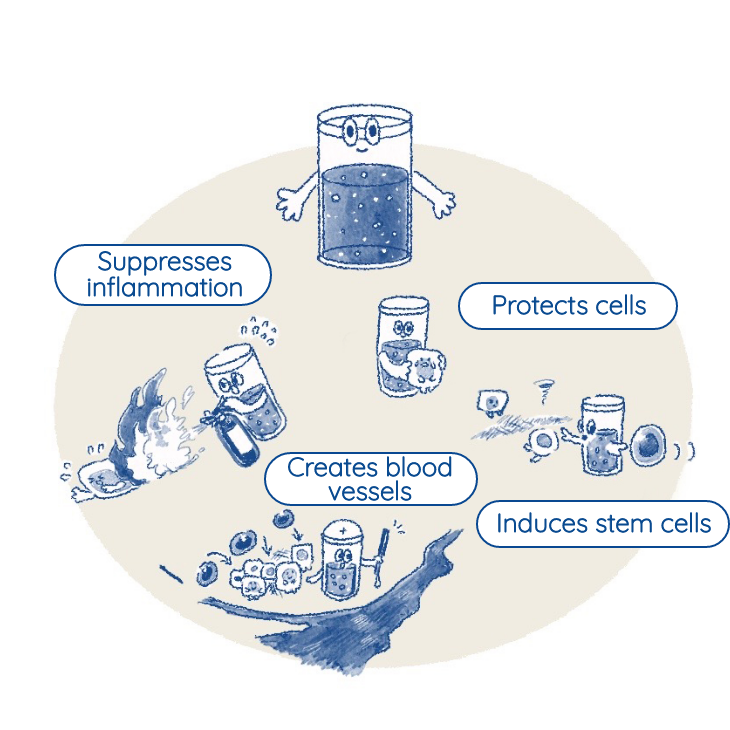
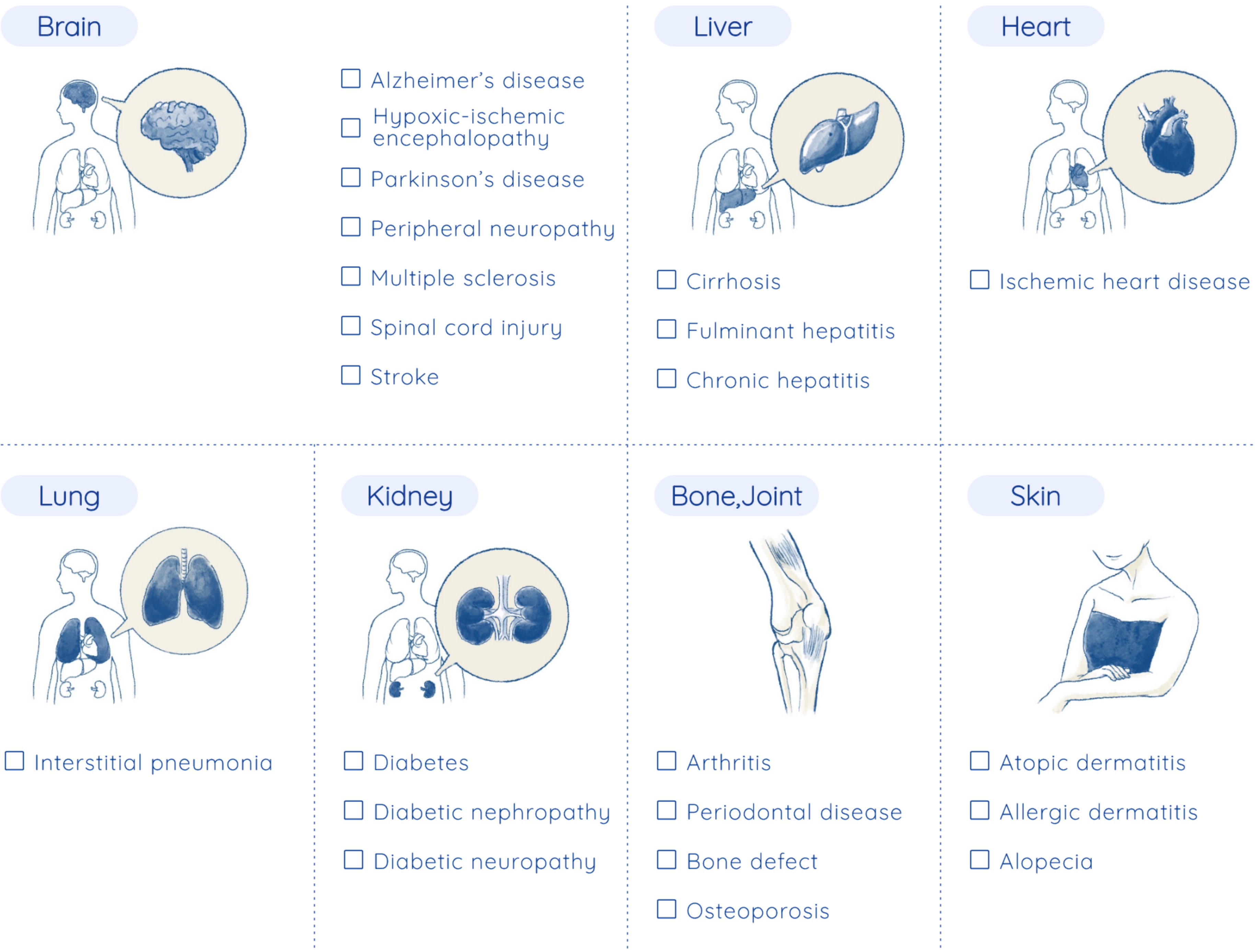
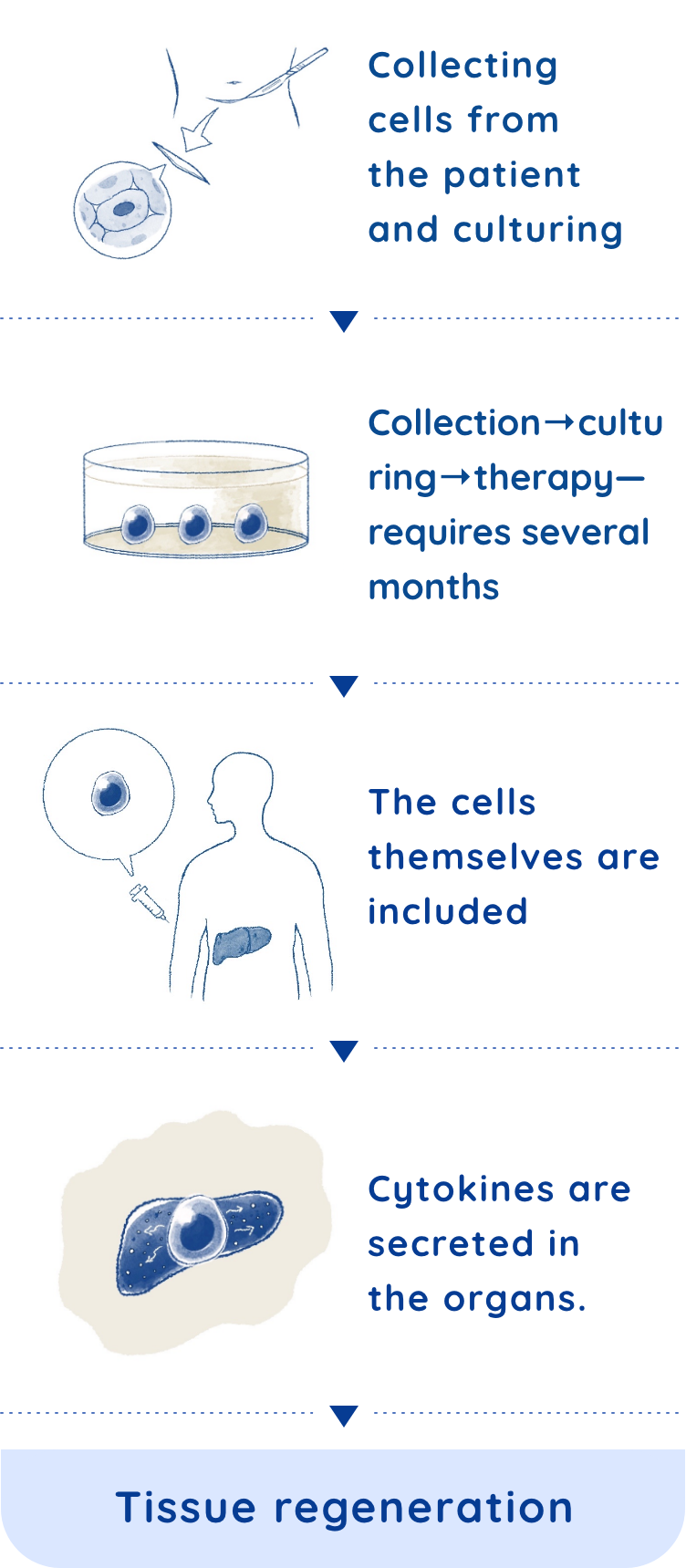
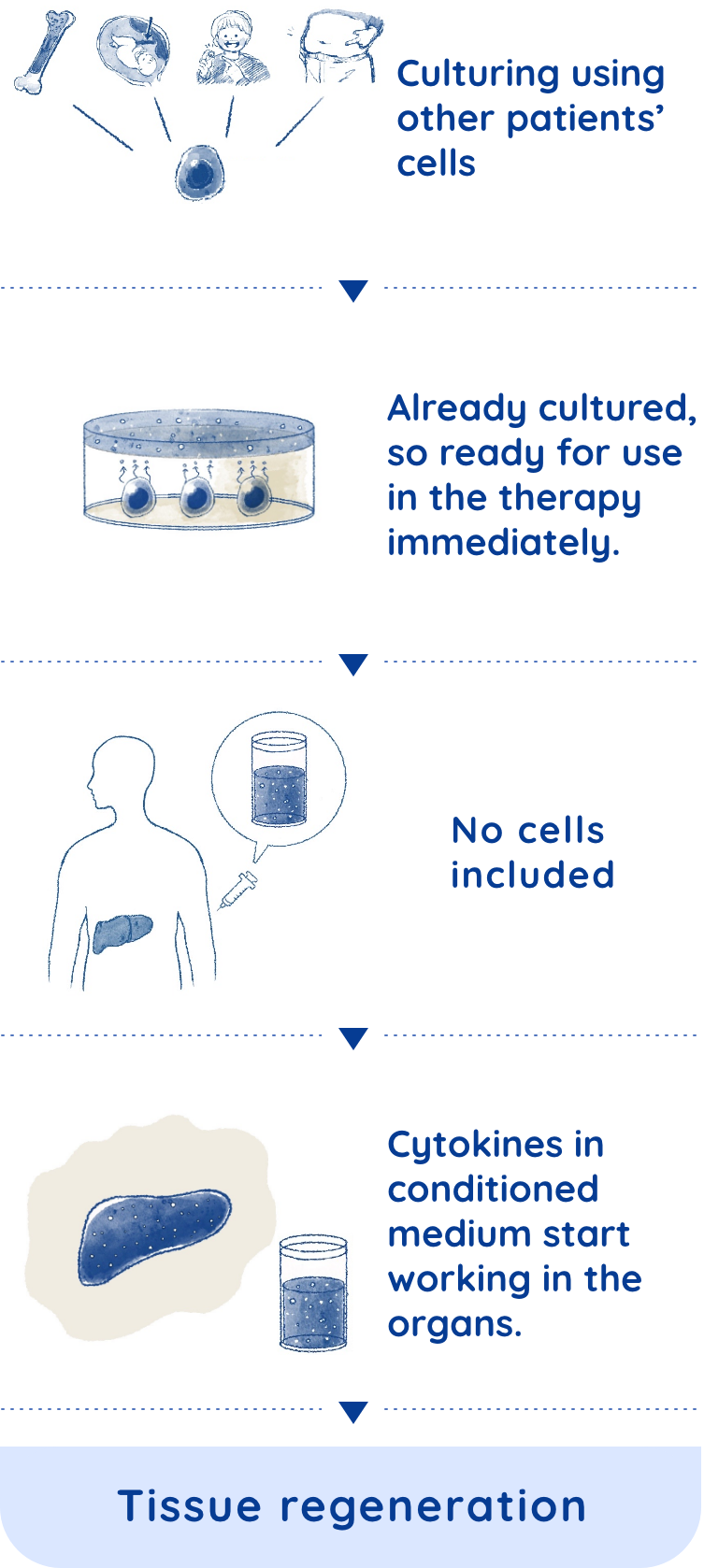
Column This "Regenerative Ability" — why do lizards’ tails grow back?
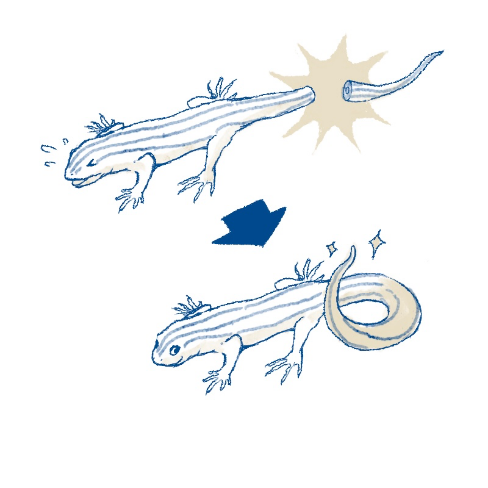
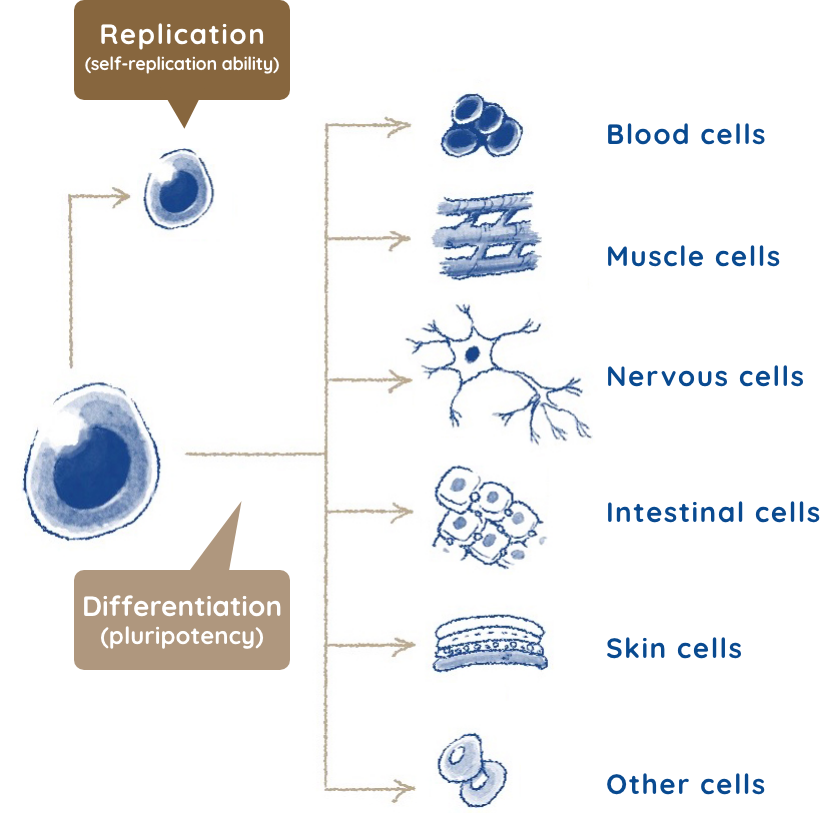
We all know of lizards’ ability to shed their tails to escape from predators or when they feel threatened, and of their ability to grow their tails back from the cut part. This grows back to the same size as the original tail. Since so many stem cells are contained in the lizard’s tail, they begin to gather all at once and correctly regenerate the lost part of the tail.
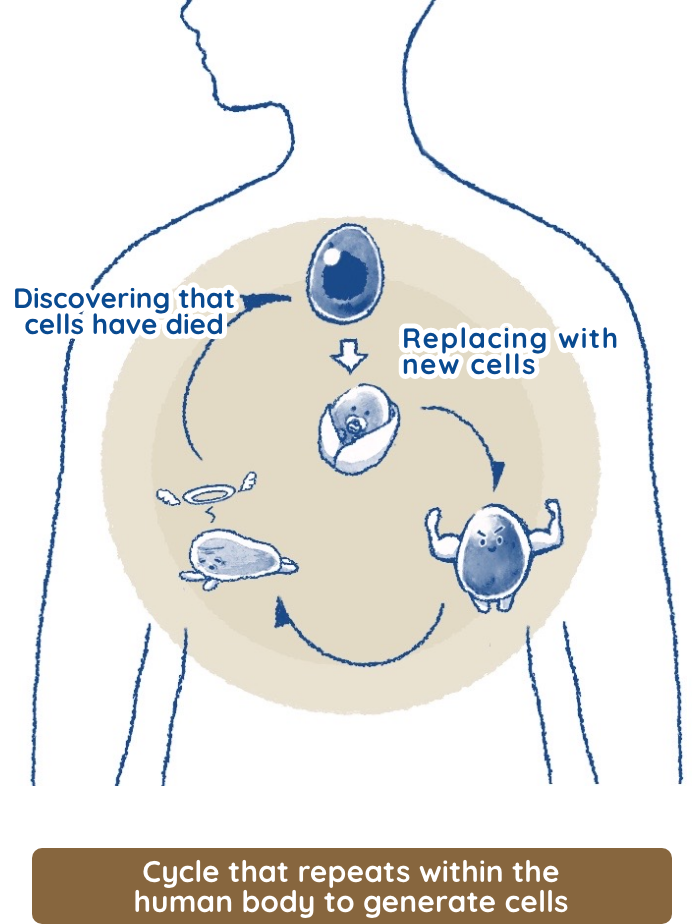
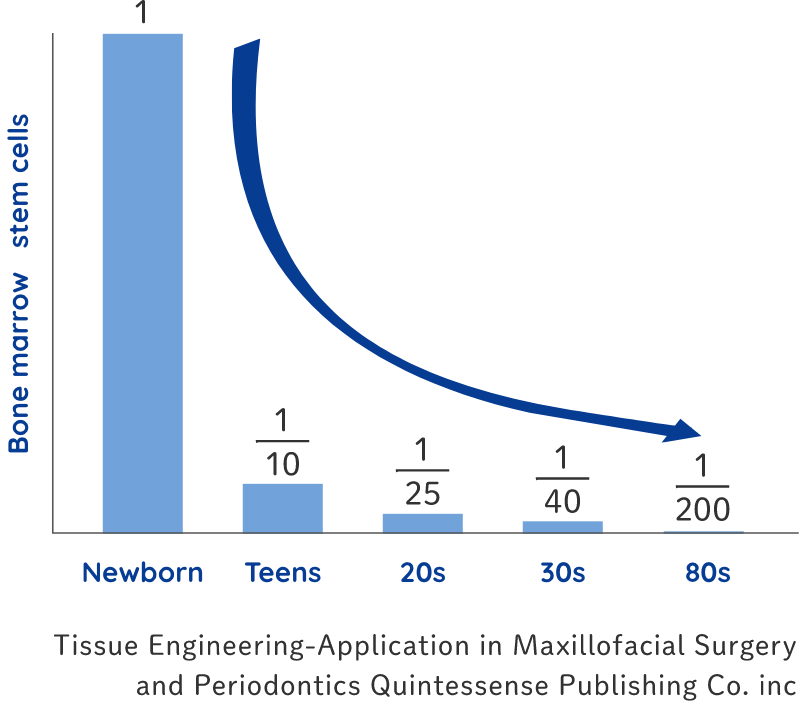
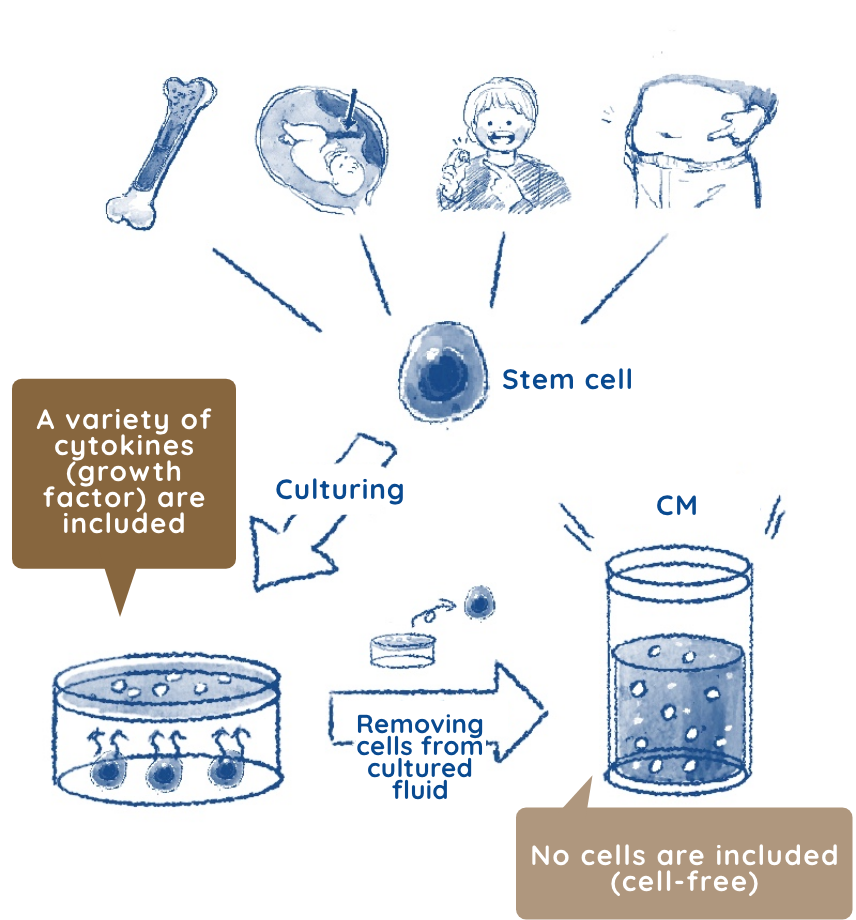
If humans had the same regenerative abilities as lizards, then we could probably recover amputated hands or legs. We, however, do not have as many stem cells nor the same regenerative abilities. But we do have some regenerative abilities, such as healing cuts on the skin, connecting broken bones, and regenerating partially removed livers.Thus, the key factors in this regeneration system are stem cells. Also, we know the numbers of stem cells decrease with age. Since newborns have many stem cells and a high ability to regenerate, they can heal quickly, even from broken bones or cuts to their skin. This is because their bodies have a lot of stem cells, and when injured, their bodies can create and supply many cells that differentiate into skin.